Rewolucja w polskim ciepłownictwie. Czy OZE ma szansę zastąpić węgiel w produkcji ciepła?
Energy transformation, including the transformation of the heating sector, is one of the key challenges facing Poland in the coming years.
The heating sector is a particularly important, though often overlooked, area.
The latest figures from 2022 shed light on the current status and prospects for changes in our country’s heat production.
Heat production structure – what do the numbers say?
Analysis of the 2022 data shows that coal fuels still dominate heat production in most provinces.
We see particularly high shares of coal in the Silesian, Lublin and Łódź provinces, where it exceeds 80% of total production.
At the same time, we see a growing role for gaseous fuels, especially in Lubuskie and Podlaskie provinces.
Interestingly, the share of RES in heat production is still relatively low, although some regional differences can be seen.
The highest percentage of RES was recorded in Podlaskie, Lubuskie and Mazowieckie provinces, which may indicate local initiatives and policies supporting green energy.

Changes over the years
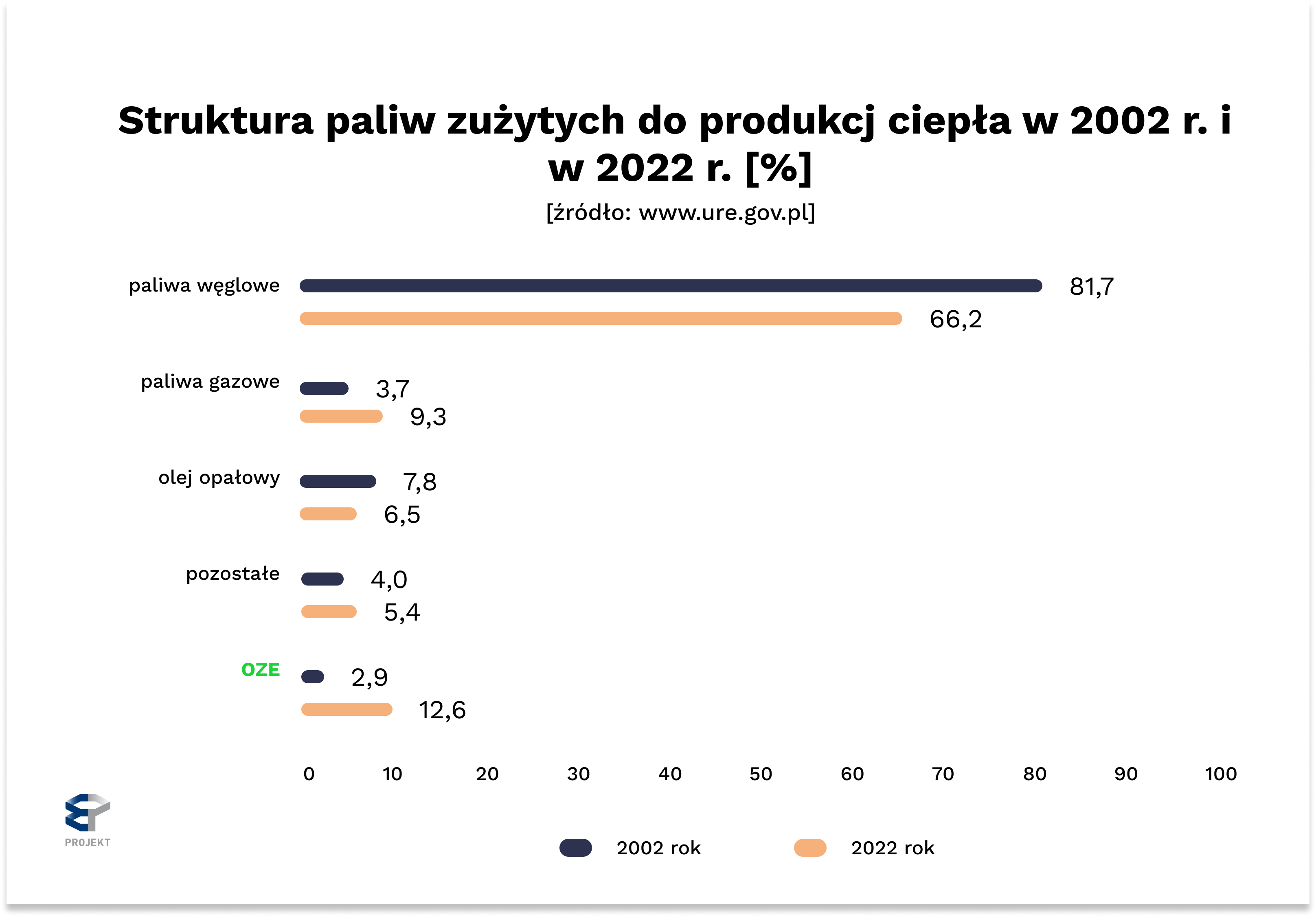
Comparing data from 2002 and 2022, we can observe some positive trends.
The share of coal fuels in the overall energy balance fell from 81.7% to 66.2%.
During the same period, the share of RES increased significantly – from 2.9% to 12.6%.
This shows that the energy transition in the heating industry is progressing, although there is still a long way to go.
Regional differences and their causes
The variation in the structure of heat production between provinces is interesting.
This may be due to several factors:
- Availability of local energy resources
- The state of the district heating infrastructure
- Regional policy and local initiatives
- Environmental awareness of residents and local authorities
For example, the high use of RES in the Podlaskie region can be linked to the availability of biomass from local forests and agriculture.
Investments in renewable energy sources to decarbonize the district heating system contribute significantly to reducing emissions and improving the quality of life of residents.
Challenges and opportunities
The main challenges facing the decarbonization of the heating industry are:
- High cost of infrastructure upgrades
- Dependence on imports of RES technologies
- Need to retrain coal workers
At the same time, the transformation brings opportunities:
- Development of local RES industry
- Improve air quality and health of residents
- Enhancing energy security
Best practices
It is worth noting positive examples of system heat production. The city of Slupsk in the Pomeranian Voivodeship is successfully implementing a program to use biomass for heating. Bielsko-Biala, on the other hand, is investing in heat pumps and geothermal.
Future prospects: renewable energy sources
According to Poland’s Energy Policy until 2040, it is planned to increase the share of RES in the heating sector to 28.4% by 2030, which is crucial for the transformation of Poland’s heating sector towards low-carbon heat generation. This is an ambitious goal, requiring significant investment and systemic change.

Summary
The data clearly show that the energy transition in the Polish heating industry is progressing, but we are still at the beginning of the road. Accelerating investment in RES, upgrading infrastructure and educating the public will be key. Carbon dioxide emissions will be reduced by upgrading heat sources to low-carbon ones, effectively decarbonizing the sector and meeting climate goals.
The future of Poland’s heating sector depends on all of us – from political decisions, to the actions of business, to the everyday choices of consumers. Are we ready for this green revolution?


